Refractive Surgery
Understanding Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery is a group of procedures designed to correct common vision problems—such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism—by reshaping the cornea. This can reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses, helping patients achieve clearer, more natural vision.
Benefits of Refractive Surgery
Refractive Surgery
- Refractive Surgery
- Post-Operative Care After Refractive Surgery
- Freedom from Glasses and Contacts: Many patients experience reduced dependence on corrective eyewear.
- Quick Procedure and Recovery: Most refractive surgeries are done on an outpatient basis with a fast recovery time.
- Improved Quality of Life: Enhanced vision can boost confidence and simplify daily activities.
Types of Refractive Surgery
There are several advanced techniques available today. Here are the most commonly performed methods:
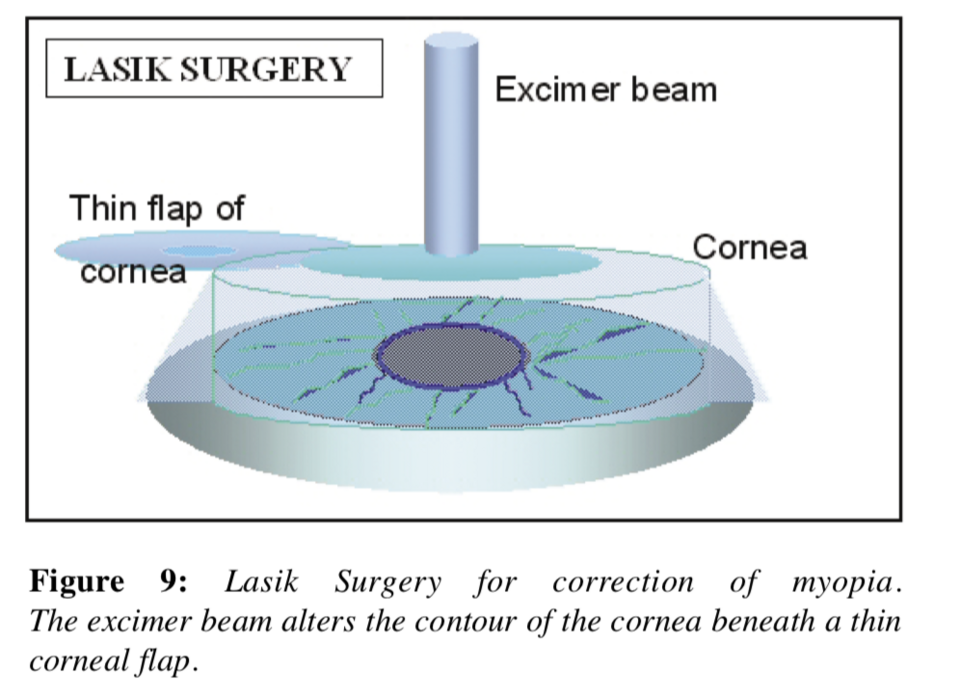
1. LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis)
- How it Works: A thin flap is created on the cornea, and an excimer laser reshapes the underlying tissue.
- Benefits: Quick recovery and minimal discomfort.
- Ideal For: Correcting nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism.
2. PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy)
- How it Works: The outer layer of the cornea is gently removed, and the excimer laser is applied directly to reshape the cornea.
- Benefits: A great option for patients with thinner corneas.
- Recovery: Takes slightly longer than LASIK as the epithelial layer regenerates.
3. SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction)
- How it Works: A femtosecond laser creates a small lenticule inside the cornea, which is then removed through a tiny incision.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive with a very small incision and rapid recovery.
- Ideal For: Primarily for patients with myopia (nearsightedness) and astigmatism.
4. RLE (Refractive Lens Exchange)
- How it Works: Similar to cataract surgery, the eye’s natural lens is replaced with an artificial lens.
- Benefits: Often recommended for patients with severe refractive errors or presbyopia.
- Ideal For: Individuals who may not be ideal candidates for corneal reshaping procedures.
Preoperative Evaluation
Before undergoing refractive surgery, patients will have a comprehensive eye exam, which may include:
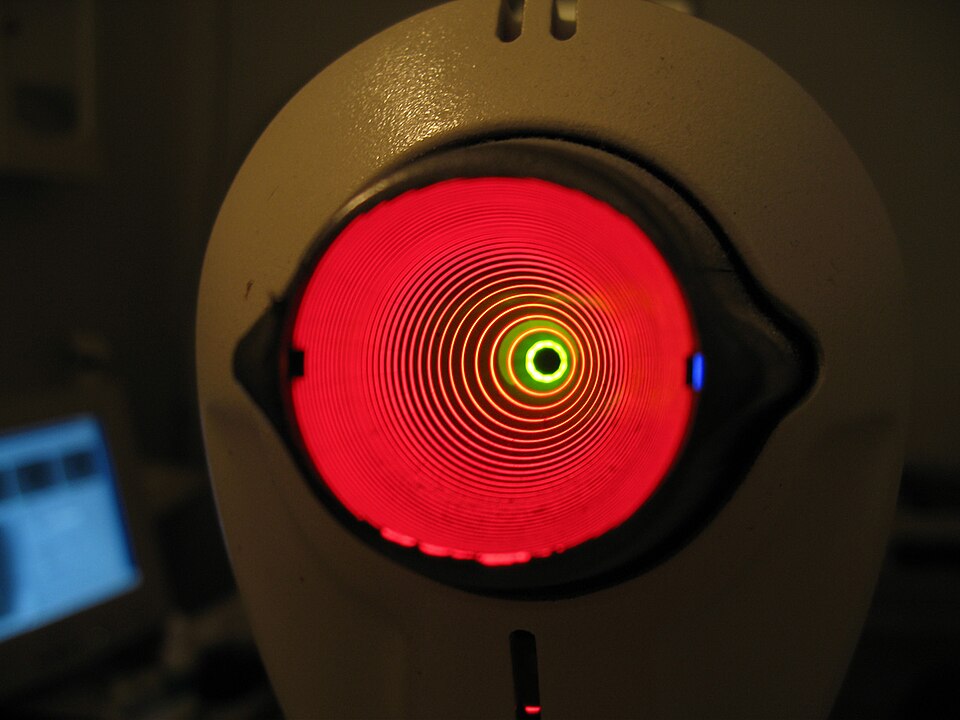
- Corneal Topography: Maps the curvature of the cornea.
- Pupillometry: Measures pupil size in different light conditions.
- Refraction Assessment: Determines the degree of refractive error.
- Ocular Health Evaluation: Ensures there are no underlying issues (e.g., dry eye, keratoconus) that could impact the surgery.
The Refractive Surgery Procedure
During the Procedure:
- Preparation: Numbing eye drops are used to ensure comfort.
- Laser Application: Depending on the method (LASIK, PRK, or SMILE), a laser reshapes the cornea with precision.
- Flap Creation (if applicable): For LASIK, a thin corneal flap is created before laser treatment.
- Completion: Once the corneal shape is adjusted, the flap (if created) is repositioned, or the epithelial layer regenerates naturally in PRK.
Postoperative Experience:
- Immediate: Patients may notice improved vision within hours; mild discomfort or light sensitivity is common.
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups ensure proper healing and fine-tuning if necessary.
- Recovery: Most individuals return to normal activities within a few days, with full stabilization in a few weeks.
Potential Risks and Considerations
Like all surgical procedures, refractive surgery has potential risks:
- Temporary dry eyes or glare
- Fluctuating vision during the healing period
- In rare cases, undercorrection or overcorrection may require enhancements
- Not everyone is a candidate—thorough evaluation is essential
Your ophthalmologist will discuss these risks and tailor the approach based on your eye health and vision needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
The changes made to the cornea are permanent; however, natural aging or other eye changes might affect vision over time.
Many patients achieve 20/20 vision without glasses, though some may still need glasses for very specific tasks such as reading or night driving.
Refractive surgeries are generally painless due to the use of anesthetic eye drops. Most discomfort is temporary and mild.
Many patients see significant improvements within 24–48 hours, though full stabilization may take a few weeks.
Refractive Surgery
1. LASIK Procedure Diagram
2. Corneal Topography Image

3. Illustration of the SMILE Procedure
Patient Guide Download
Want to read more? Download this trusted guide from the National Eye Institute:
Refractive Surgery
- Refractive Surgery
- Post-Operative Care After Refractive Surgery
